A medical degree from RCSI & UCD Malaysia Campus could be your first step to becoming a doctor. We provide our students with the assistance, skills and knowledge to strive in their future careers. With our internationally-recognised medical degree, we are passionate about shaping you into being a healthcare professional and succeed in serving your patients in the future.
One of the most challenging decisions among medical students is picking the right profession and outlining how to get to where you want to be. Having the right facts and information is vital in making decisions for your future medical career pathway. With more than 200 healthcare occupations in the industry today, there are many factors to help you identify the career path that will fit you best with the kind of lifestyle you desire.
As a well-known medical university in Malaysia, we are here to enlighten you with what your future in a healthcare career will look like with the following list of major medical professions. At the end of this article, you will learn about the different types of medical careers and the responsibilities you will uphold throughout your medical tasks.
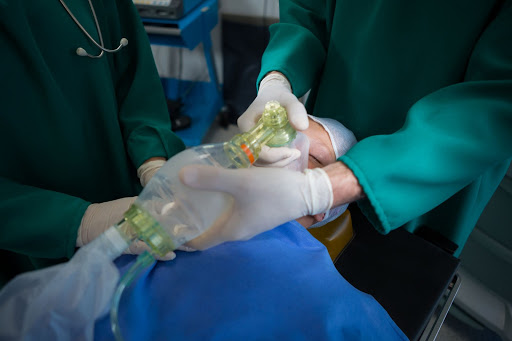 Anaesthesiologist
Anaesthesiologist
An anaesthesiologist is a doctor who practices anaesthesia, specialising in developing anaesthetic plans and the administration of anaesthetics. An anaesthesiologist plays an important role in medical care before, during and after surgery.
Responsibilities:
- administer appropriate anaesthetics to numb pain or sedate patients during surgery
- take note of patients’ consciousness level, body temperature and vital signs
- manage patients’ emotional stress during surgical and medical procedures
- emergency clinical management of various fluid, electrolyte, and metabolic disturbances
 Cardiologist
Cardiologist
A cardiologist is a doctor who specialises in the treatment of the cardiovascular system, mainly the heart and blood vessels. Besides treating heart-related conditions, they focus on counselling individuals regarding how to prevent heart-related conditions.
Responsibilities:
- identify and treat heart rhythm disturbances, heart-related disease and heart failure
- management of disorders of the cardiovascular system such as ischemic heart disease, cardiac dysrhythmias, cardiomyopathies, valvular heart disease, pericarditis and myocarditis, endocarditis, congenital heart disease in adults, hypertension, and disorders of the veins, arteries, and pulmonary circulation
- evaluate a patient’s family medical history to determine potential risk factors
- undergo cardiac catheterization, balloon angioplasty or other types of simple heart surgery
 Family Medicine Specialist
Family Medicine Specialist
A Family Medicine Specialist is a doctor who manages common and long-term illnesses in children, adults and the elderly. They focus on patients’ overall health and well-being. Although the job scope of family medicine is broad, it is a precise discipline with a blend of biomedical, behavioural, and social sciences.
Responsibilities:
- provide general medical cares to patients in medical settings such as clinics, hospitals, and private offices
- diagnose and treat the illness that occurs in everyday life
- provide annual check-ups and preventative care services
- first to recognise major health problems and collaborate with other medical specialists to arrange appropriate specific care
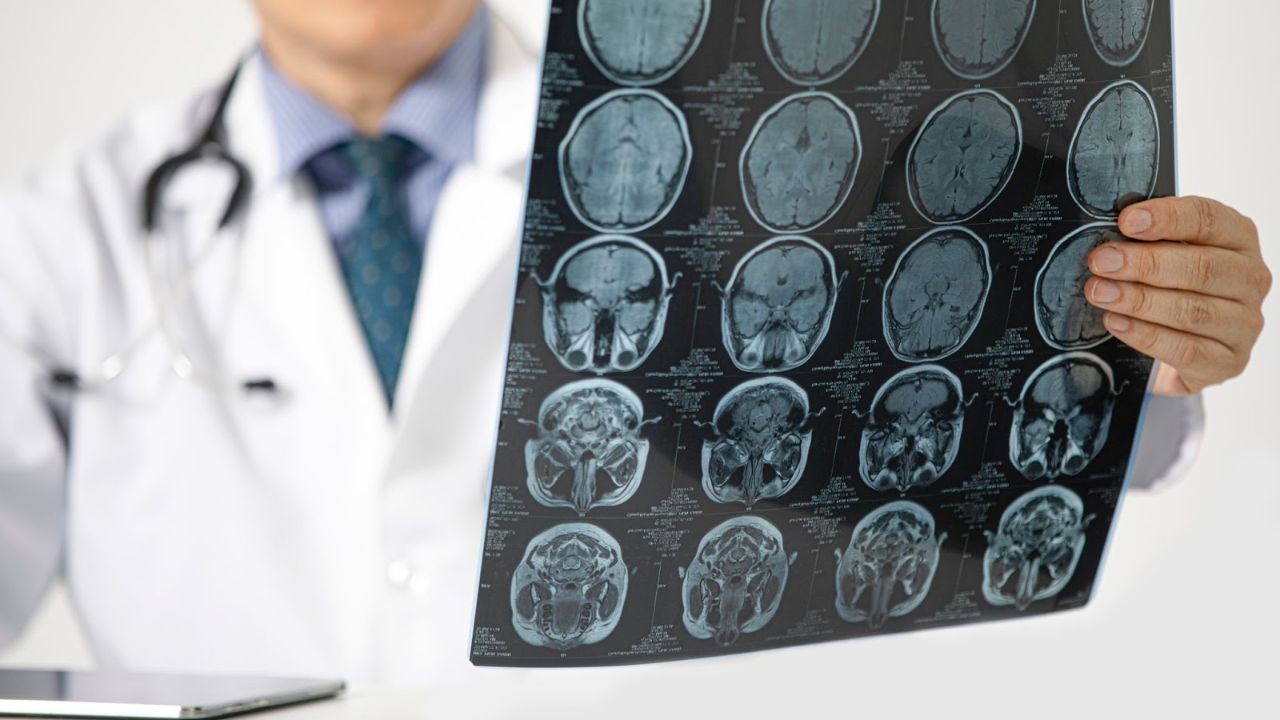 Neurologist
Neurologist
A Neurologist is a doctor who focuses on the care of the nervous system which includes the brain, nerves and spinal cord. Moreover, they are specialists in the anatomy, functions, and organic disorders of nerves and the nervous system.
Responsibilities:
- specialise in diagnosing and treating conditions that affect the nervous system
- treatment of diseases or impaired functions related to the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, muscles, autonomic nervous system, and the blood vessels that relate to these structures
- care for patients who have a variety of disorders, including headaches, strokes, seizure disorders, multiple sclerosis, dystonia, muscular dystrophy, peripheral nerve disease, learning disorders, traumatic injuries to the nervous system, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- engage in neurological rehabilitation
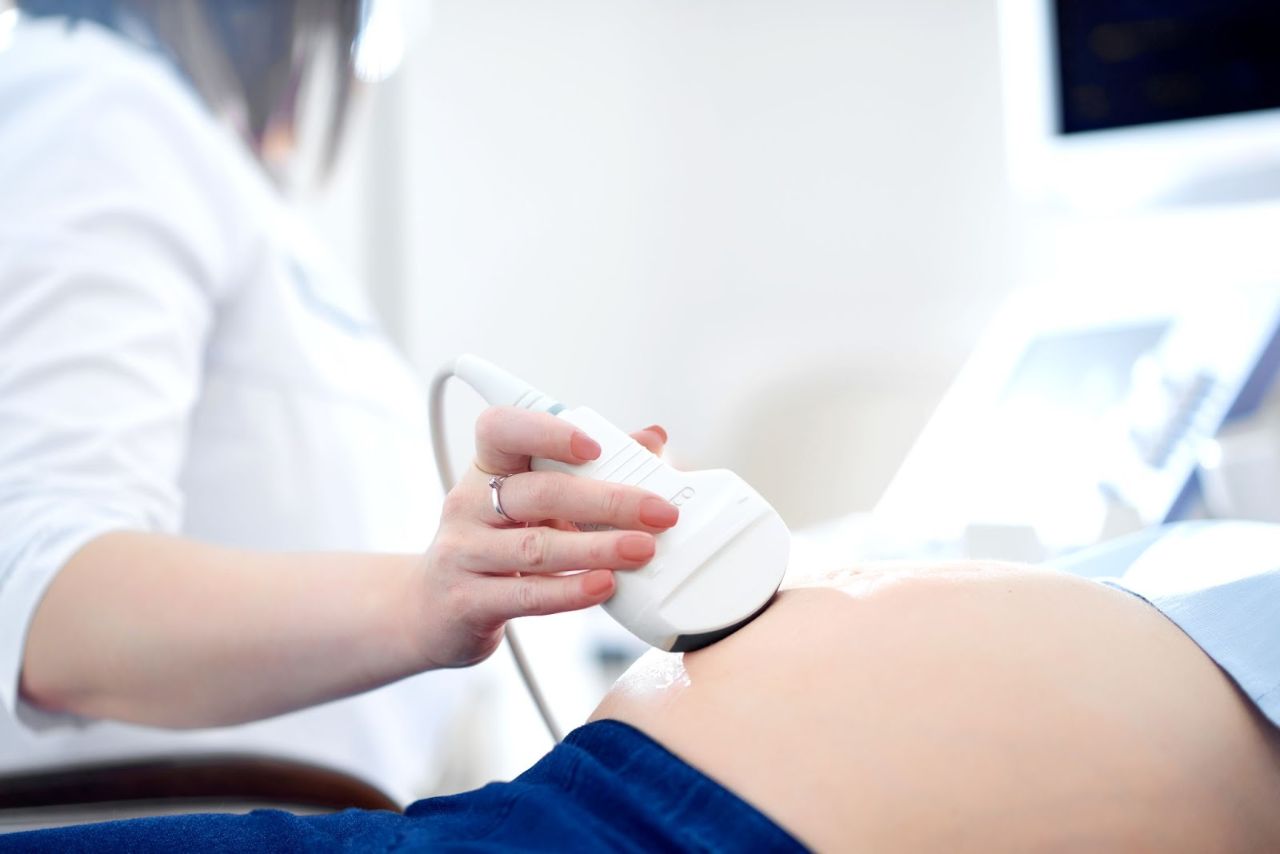 Obstetrician and Gynecologist
Obstetrician and Gynecologist
An Obstetrician and Gynecologist (OB/GYNs) is a doctor who provides care related to pregnancy, childbirth, and the female reproductive system. Obstetricians focus more on the care of women before, during, and after childbirth; whereas gynecologists involve themselves more in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the female reproductive system, breasts, and associated disorders.
Responsibilities:
- help to prevent diseases of women, especially those related to the female reproductive system
- monitor the health of the mother and the safety of the fetus during a pregnancy
- maintain long-term relationships with female patients
- practice other skills such as laparoscopic surgery, endocrinology, and preventive medicine
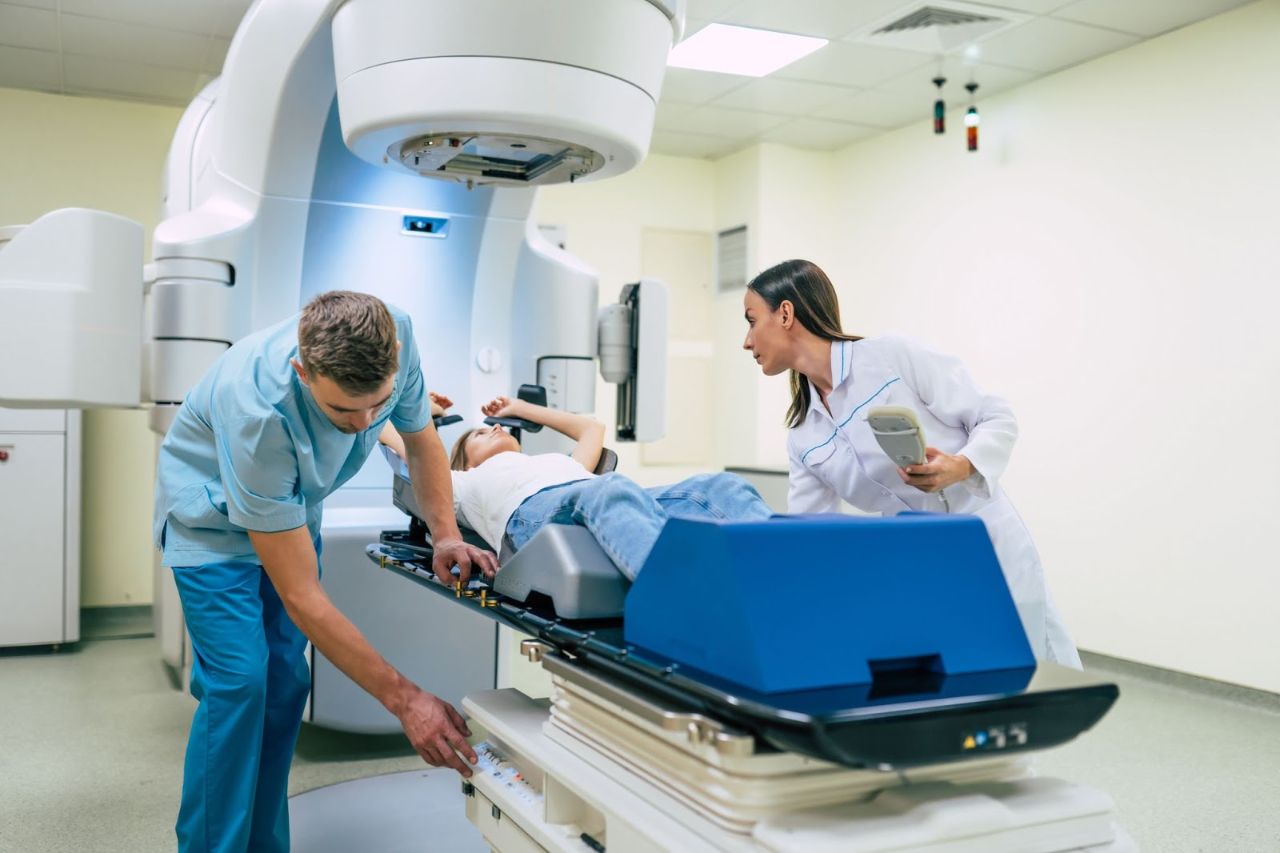 Oncologist
Oncologist
An Oncologist is a doctor who cares for cancer patients through the diagnosis and treatment of cancers. They spend time with cancer survivors with follow-up sessions. Oncologists possess an in-depth understanding of the symptoms related to different types of cancers.
Responsibilities:
- focus on the diagnosing and treating of benign tumours and other forms of cancer
- making an accurate cancer diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate type of cancer treatments
- study a range of test results, such as CAT or MRI scans, biopsies, and ultrasounds
- provide ongoing care and consultation for patients during and after their treatment
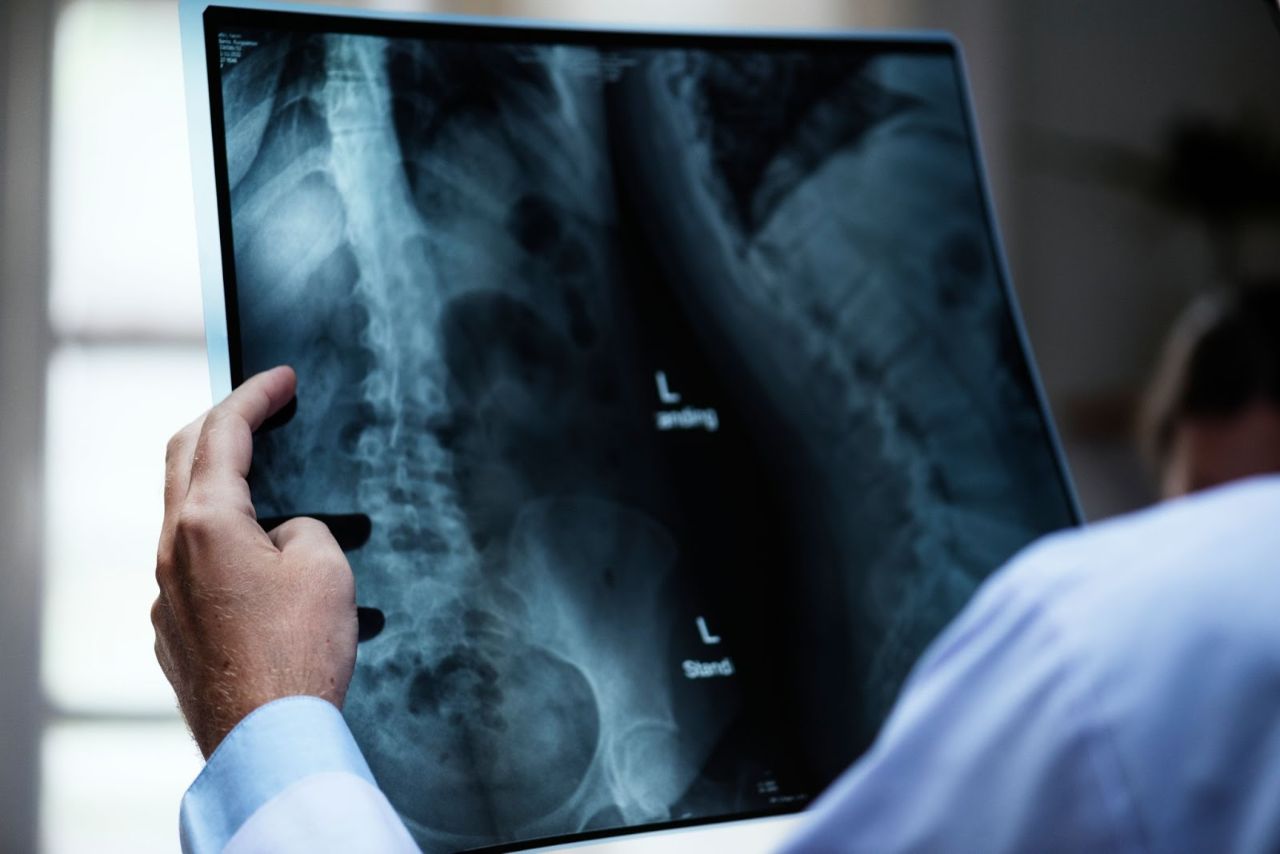 Orthopaedist
Orthopaedist
An orthopaedist is a doctor who takes care of the musculoskeletal system, such as bones, joints, ligaments, nerves, and tendons. Orthopaedic doctors recommend non-surgical treatments like resting, physical therapy or rehab, medications or injections. They will advise patients with the potential outcomes of having or postponing a surgery, whilst taking into account your age and day-to-day activities.
Responsibilities:
- diagnose and treat injuries that are caused by physical activities
- correct congenital or functional abnormalities of the bones with casting, bracing and surgery
- help in managing bones conditions like arthritis or osteoporosis that usually get worse over time
- assist in avoiding discomfort from using a muscle or joint too often
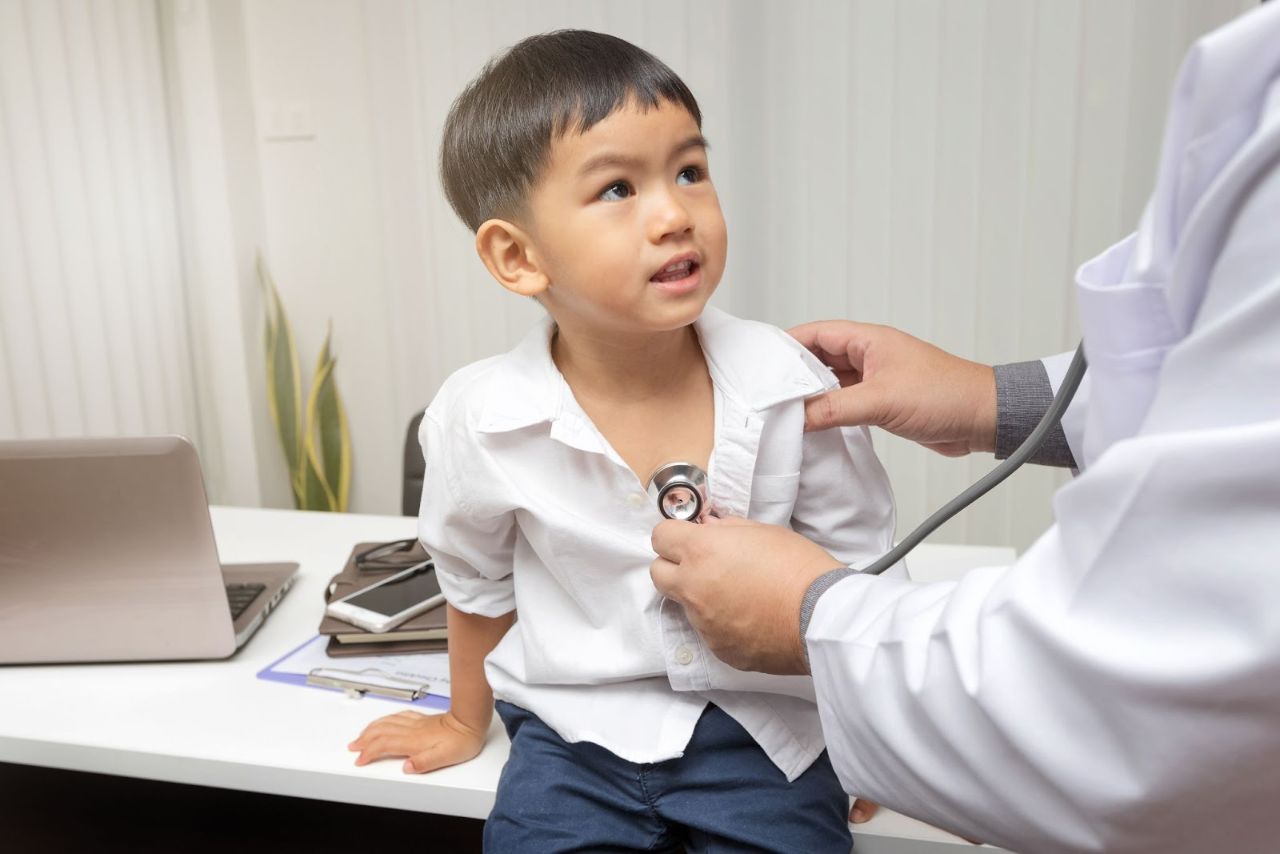 Paediatrician
Paediatrician
A Paediatrician is a doctor who cares for children from birth to adolescence or young adulthood. Their consolation rooms are usually bright and cheerful, which are appealing to children.
Responsibilities:
- diagnose and treat health problems specific to children such as common illnesses, minor injuries, infectious diseases, and provide vaccinations
- care about the physical, emotional, and social health of infants, children, teenagers, and young adults
- determine the biological, social, and environmental impacts on the developing child
- interact with parents or guardians and educate them about the child’s normal health and growth
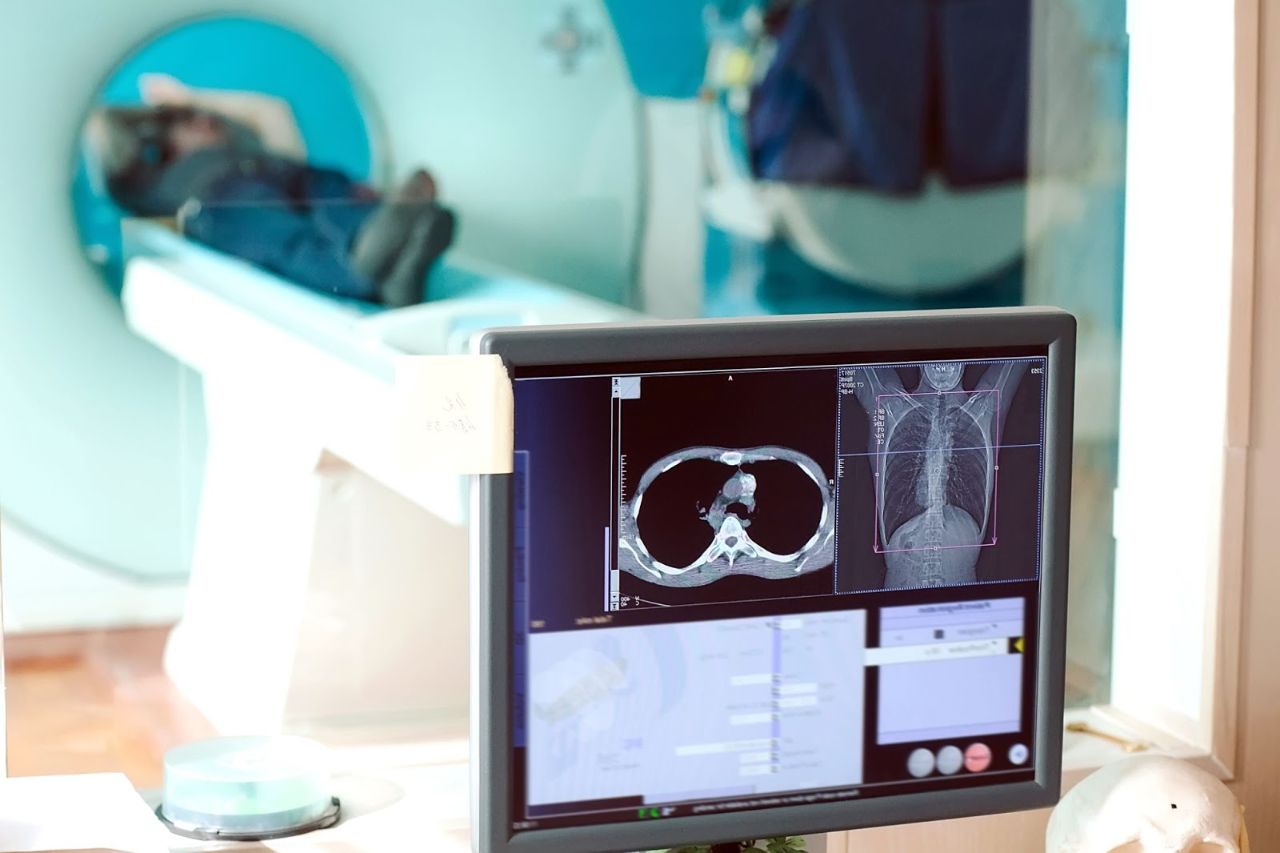 Radiologist
Radiologist
A Radiologist is a doctor who uses x-rays and other imaging technologies to diagnose and identify physiological disorders and conditions. Besides x-rays, they utilize medical radiology procedures such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) and ultrasound.
Responsibilities:
- scan a patient’s body for cancer cells or look for breaks in fractures in accident victims
- treat certain conditions using an extensive variety of imaging techniques
- diagnose serious heart conditions
- act as important consultants to the primary physician
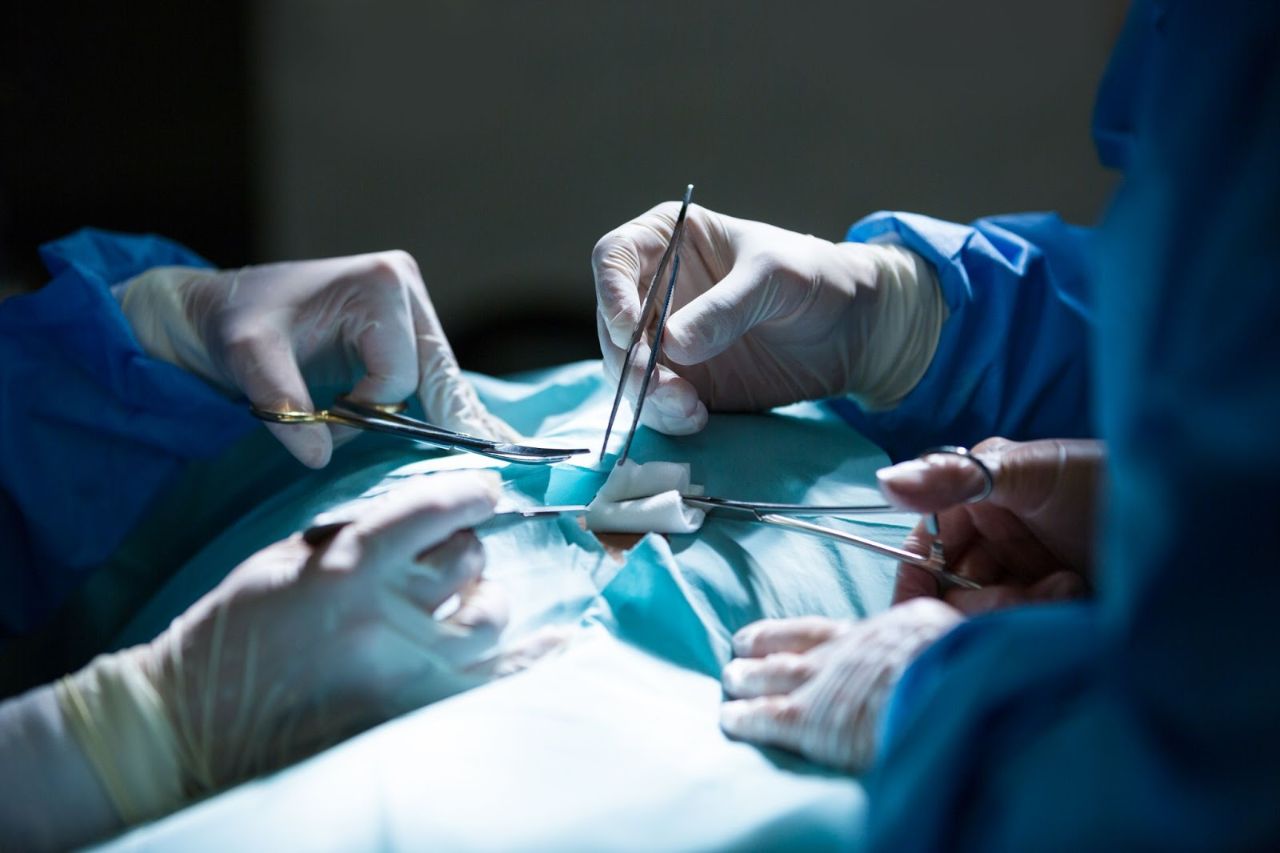 Surgeon
Surgeon
A Surgeon is a doctor who performs operations in order to save patients’ lives. Surgery comes with different specialities such as general surgery, neurosurgery, cardiovascular surgery, oral surgery, ENT surgery and cardiovascular surgery.
Responsibilities:
- treat patients with injuries, diseases, and deformities in different body areas
- using a variety of instruments to repairs bone and tissue at the operating table
- examine patients, perform and interpret diagnostic tests, and counsel patients on preventive healthcare
- possess excellent technical and problem-solving skills besides staying calm under time and mental pressures.
At RCSI & UCD Malaysia Campus, we believe that you are an asset in changing people’s lives. Become a healthcare expert you aspire to be with one of these rewarding medical careers as they will bring a great impact on our healthcare system and at the same time, they will present you with career satisfaction like no other.
We are always ready to help you embark on your medical journey and provide more insights into different areas of Medicine. Reach out to us and find out your possible medical studies route ranging from undergraduate studies, postgraduate studies, pre-clinical studies, scholarships, medical courses or any other information.











